 |
АвтоАвтоматизацияАрхитектураАстрономияАудитБиологияБухгалтерияВоенное делоГенетикаГеографияГеологияГосударствоДомДругоеЖурналистика и СМИИзобретательствоИностранные языкиИнформатикаИскусствоИсторияКомпьютерыКулинарияКультураЛексикологияЛитератураЛогикаМаркетингМатематикаМашиностроениеМедицинаМенеджментМеталлы и СваркаМеханикаМузыкаНаселениеОбразованиеОхрана безопасности жизниОхрана ТрудаПедагогикаПолитикаПравоПриборостроениеПрограммированиеПроизводствоПромышленностьПсихологияРадиоРегилияСвязьСоциологияСпортСтандартизацияСтроительствоТехнологииТорговляТуризмФизикаФизиологияФилософияФинансыХимияХозяйствоЦеннообразованиеЧерчениеЭкологияЭконометрикаЭкономикаЭлектроникаЮриспунденкция
Light natural and polarized. Polaroids
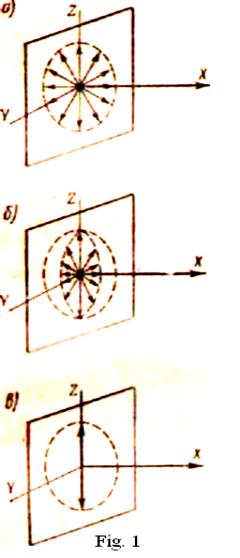 In a cross-section wave fluctuation can occur in any directions laying in a plane, perpendicular to a direction of distribution of a wave. (In mechanical wave - fluctuation of substance particles, and in electromagnetic wave - vectors of intensity of a field).
In a cross-section wave fluctuation can occur in any directions laying in a plane, perpendicular to a direction of distribution of a wave. (In mechanical wave - fluctuation of substance particles, and in electromagnetic wave - vectors of intensity of a field).
If directions of fluctuations thus randomly vary, but their amplitudes in all directions are identical (fig.1,) such wave refers to natural. If fluctuations occur only in one constant direction such wave refers to linearly polarized.
If fluctuations occur in various directions, but in the certain directions amplitude of fluctuations is more, than in others (fig.1,) that such wave refers to partially polarized. In natural conditions all kinds of waves can be. Artificial polarization of wave can be carried out, passing it through the special device (depending from natural of waves), which is named polarizer of a wave. For a wave on an elastic cord as a polarizer the crack between two parallel surfaces (fig. 2) can serve. If in an index point of a cord to raise fluctuations in various directions, after a crack they will occur only in a plane, conterminous with a plane of a crack. If a crack to turn on some corner around of an axis, conterminous with a direction of a cord on a corresponding corner the plane of fluctuations will turn also, the crack polarizes a wave in its plane.
Let's put on a way of the polarized wave the second crack. If planes of cracks coincide (fig. 2, а) fluctuations will pass through the second crack without change of amplitude.
If the second crack to turn on some corner also position of a plane in which there are fluctuations and amplitude accordingly will change and fluctuations will decrease (fig. 2, b)  ,
,
where  - amplitude of fluctuations before a crack
- amplitude of fluctuations before a crack

Fig.2
At turn of the second crack on corners from 0 up to 900 amplitude of the fluctuations which have been last through a crack, changes from the maximal size up to zero. Therefore, rotating the second crack around of an axis, it is possible to define position in space of a plane of fluctuation of the polarized wave on change of amplitude of fluctuations. In this connection the second crack refers to as the analyzer of a wave.
At polarization of light vector Е of intensity of an electric component of a field name a light vector of a wave, and a plane of its fluctuations - a plane of fluctuations of a wave.
It is possible to consider, that in one certificate of radiation electron in atom lets out plainly the polarized light wave in which fluctuations of a light vector occur in one plane.
One certificate radiation proceeds during 10-8 sec, thus the group of waves is formed. Then the atom radiates new group of waves, the direction and a phase of light vector are not connected with the previous group.
The light wave radiated by a body as a whole, is formed in result of addition of the waves radiated by set of atoms with various and randomly varying, on time by orientation light vectors. Also the direction of a light vector of a total wave accordingly varies. Thus all directions for a light vector are equivalent, the wave is natural, or non polarized. All natural light sources radiate non polarized light.
Experience shows, that linear polarization of natural light, especially partial, occurs at its reflection, refraction and dispersion. It is connected by that the secondary waves radiated by atoms of substance under influence of the falling wave, similarly to the micro-vibrator, radiate light in various directions non-uniformly. Therefore at formation reflected or refracted (and especially scattered wave) waves, amplitude of fluctuations in it in same directions have the greatest size, and in others considerably smaller size. Thus, polarized light - the phenomenon rather widespread, however we do not notice it, as our eye does not distinguish polarized light from natural. Therefore all the supervision connected with polarization of light, are made by means of corresponding devices.
At the device of polarizers for light the phenomenon of double refraction in crystals is usually used. Anisotropy is characteristic of crystals. Distinction of physical properties, including optical, in the certain directions in a crystal. Optical anisotropy, a difference in speed of distribution of light, is connected by that the compelled fluctuations of electrons in the certain directions are raised by a falling light wave easier, than in others, and then speed of distribution of a total wave of a crystal in these directions is different.
 Direction on which optical properties of a crystal most differ, is named an optical axis of a crystal. The optical axis can be lead through any point of a crystal. The plane lead through the falling beam and an optical
Direction on which optical properties of a crystal most differ, is named an optical axis of a crystal. The optical axis can be lead through any point of a crystal. The plane lead through the falling beam and an optical
Fig. 3.
axis, lead to a point of falling, refers to as the main plane of a crystal. In connection with optical anisotropy the certain crystals have a phenomenon of double refraction. The narrow light bunch (А Б on fig. 3, a), falling on a surface of a crystal, is divided into two bunches (БД and БЕ БЕ on fig. 3, a), passing through a crystal in various directions. To intensity of each beam it is equal to half of intensity of a falling bunch. If through such crystal to look for its contours will be observed dual (fig. 3, b).
In an anisotropic crystal at falling a light wave in each point of its surface there are simultaneously two elementary waves (fig. 4.): one as it is usual, - spherical, and the second - elliptical. In a crystal two are formed the resultant waves are named ordinaryo and unusualе, having various phase speeds and directions distribution to a crystal (On fig. 4: АВ - front of a falling flat wave, MN-an optical axis concerning which the elementary wave is focused elliptical, DC - front of ordinary wave and FC - front of unusual wave in a crystal).
Both waves are completely polarized, fluctuations of a light vector of a unusual wave occur in the main plane of a crystal, and ordinary - in a perpendicular plane. One of these waves (more often unusual) also is used in polarizing devices as a source of polarized light (the second wave is extinguished).
 Nicol prism is used in precision devices for this purpose. Doubly refracting crystals possess property dichroism - various absorption of light depending on a direction of a plane of its fluctuations. In these crystals ordinary beams
Nicol prism is used in precision devices for this purpose. Doubly refracting crystals possess property dichroism - various absorption of light depending on a direction of a plane of its fluctuations. In these crystals ordinary beams
are completely absorbed.
Fig. 4.
Light which has passed through a crystal, becomes completely polarized.
The device of polarizing filters, or polaroid is based on this phenomenon. They represent a transparent film which contains crystals dichroic substances, which polarizes light. During manufacturing of a film crystals are guided so that their optical axes were parallel. As a result they give polarized light with fluctuations in one certain plane.
Поиск по сайту: