 |
АвтоАвтоматизацияАрхитектураАстрономияАудитБиологияБухгалтерияВоенное делоГенетикаГеографияГеологияГосударствоДомДругоеЖурналистика и СМИИзобретательствоИностранные языкиИнформатикаИскусствоИсторияКомпьютерыКулинарияКультураЛексикологияЛитератураЛогикаМаркетингМатематикаМашиностроениеМедицинаМенеджментМеталлы и СваркаМеханикаМузыкаНаселениеОбразованиеОхрана безопасности жизниОхрана ТрудаПедагогикаПолитикаПравоПриборостроениеПрограммированиеПроизводствоПромышленностьПсихологияРадиоРегилияСвязьСоциологияСпортСтандартизацияСтроительствоТехнологииТорговляТуризмФизикаФизиологияФилософияФинансыХимияХозяйствоЦеннообразованиеЧерчениеЭкологияЭконометрикаЭкономикаЭлектроникаЮриспунденкция
Pharmacokinetic model
For the description of kinetics of changes of concentration of the medical product entered into an organism it is offered so-called pharmacokinetic model.
It is necessary for us to find laws of change of concentration of a medical product at various ways and parameters of its introduction and deducing. In a reality input and output of medicinal substances is accompanied by greater number of various processes. These are processes всасывания in a blood channel, carry of a medicine from blood to bodies, removal of a preparation from blood by kidneys.
The basic assumptions:
1. We shall not consider system of bodies through which consistently passes a medicine. We shall exclude stages of processes of input, carry, a conclusion of medicinal substance.
2. We shall not consider molecular mechanisms of processes (for example, permeability of substance, chemical transformations).
3. Processes of input and output we shall reduce by the speed.
Let's consider laws of change C (t) at various ways of introduction of a medicine
 Fig.5. Pharmacokinetic models for various ways of introduction of a medical product: unitary (a), continuous (b) both combined (c) and schedules of time dependences of concentration of a medical product corresponding them in an organism.
Fig.5. Pharmacokinetic models for various ways of introduction of a medical product: unitary (a), continuous (b) both combined (c) and schedules of time dependences of concentration of a medical product corresponding them in an organism.
1-st way. Unitary introduction of a medical product - an injection (fig. 5.а). It corresponds to a case when to the patient «have made an injection».
Let's imagine an organism as system in volume V, after introduction in which medical product in weight m0 its removal from an organism begins. Distribution of a preparation on volume is supposed uniform. Speed of removal p a preparation from an organism is directly proportional to its weight in an organism  K- factor of removal of a preparation from an organism.
K- factor of removal of a preparation from an organism.
Speed of change of weight of medicinal substance in an organism 
is equal to speed of its deducing р;  , and therefore
, and therefore 
The decision of this differential equation, in view of the entry condition, that at t=0 weight entered medicinal m=m0,  . Concentration of a medical product in an organism (for example, in blood)
. Concentration of a medical product in an organism (for example, in blood)  .
.
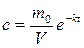 or
or  , where v -volume of blood, с0 -initial concentration.
, where v -volume of blood, с0 -initial concentration.
Concentration of a medical product in blood will continuously decrease on decreasing by the exponential law (fig. 6.а) Thus, at a unitary way of introduction of a medicine is not possible to support its constant concentration in blood.
2-nd way. Continuous introduction of a preparation with constant speed - infusion
(Fig. 6.b) (it corresponds to a case when to the patient have put a dropper).
In this case change of weight of a medical product in an organism  is defined not only with speed of its removal р, but also speed of introduction Q -quantity of the medicinal substance entered into an organism for a time unit:
is defined not only with speed of its removal р, but also speed of introduction Q -quantity of the medicinal substance entered into an organism for a time unit:  .
.
Let's solve this differential equation in view of, that at t=0 weight m=0.
Solving we shall receive this differential equation, that after a while after the beginning of introduction of a medicine constant concentration is established  . Having picked up speed of introduction of a medicine
. Having picked up speed of introduction of a medicine  , we shall reach that the optimum concentration
, we shall reach that the optimum concentration  only after any time (fig. 6. b).
only after any time (fig. 6. b).
Optimum concentration can be established in an organism instantly at a combination of the first and second ways.
3-rd way. A combination of continuous introduction of a medical product (2-nd way) to introduction loading dozes (1-st way) (fig. 6.c)
Thus the pharmacokinetic model will become: 
The graph of this dependence in a general view is presented on rice 6. If to choose introductions of medicines corresponding speed 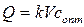 and a loading doze
and a loading doze  , constant concentration
, constant concentration  is established instantly (a direct line 2, fig.6.c)
is established instantly (a direct line 2, fig.6.c)
Thus, the pharmacokinetic model allows finding the law of change of concentration of a preparation in time at various ways of its introduction in an organism, to calculate an optimum parity between parameters of input and output of a preparation for maintenance of necessary therapeutic effect.
Поиск по сайту: