 |
АвтоАвтоматизацияАрхитектураАстрономияАудитБиологияБухгалтерияВоенное делоГенетикаГеографияГеологияГосударствоДомДругоеЖурналистика и СМИИзобретательствоИностранные языкиИнформатикаИскусствоИсторияКомпьютерыКулинарияКультураЛексикологияЛитератураЛогикаМаркетингМатематикаМашиностроениеМедицинаМенеджментМеталлы и СваркаМеханикаМузыкаНаселениеОбразованиеОхрана безопасности жизниОхрана ТрудаПедагогикаПолитикаПравоПриборостроениеПрограммированиеПроизводствоПромышленностьПсихологияРадиоРегилияСвязьСоциологияСпортСтандартизацияСтроительствоТехнологииТорговляТуризмФизикаФизиологияФилософияФинансыХимияХозяйствоЦеннообразованиеЧерчениеЭкологияЭконометрикаЭкономикаЭлектроникаЮриспунденкция
Incoterms - International Commercial Terms
The Incoterms rules are a series of international sales terms, published by International Chamber of Commerce (ICC). They are an internationally recognized standard and are used worldwide in international and domestic contracts for the sale of goods. First published in 1936, they govern where the cost of transport and risk of loss lie in international transactions. Since January 1, 2011 the eighth edition, Incoterms 2010, has had effect.
(cost of transport = who pays for the transportation
risk of loss = who bears the cost/responsibility should the cargo be damaged, destroyed, or lost)
Incoterms are standardized internationally, so if a seller tells you the something costs X US dollars FOB port Y, you both know exactly what your cost and responsibilities are. For example, you are in Kharkiv, Ukraine, and you contact a factory in Guangzhou, China to buy some hardware. The factory quotes you $5/unit, FOB Guangzhou, or $6/unit CIF Odessa.
Regulations are as follows:
EXW – Ex Works. The seller makes the goods available at his premises. This term places the maximum obligation on the buyer and minimum obligations on the seller. The Ex Works term is often used when making an initial quotation for the sale of goods without any costs included
FCA - Free Carrier. The seller delivers the goods, cleared for export, at a named place. This can be to a carrier nominated by the buyer, or to another person nominated by the buyer.
CPT – Carriage Paid To (named place of destination).
CPT replaces C&F (cost and freight) and CFR terms. The seller pays for the carriage of the goods up to the named place of destination. Risk transfers to buyer upon handing goods over to the first carrier at the place of shipment in the country of Export. The Shipper is responsible for origin costs including export clearance and freight costs for carriage to named place (usually a destination port or airport). The shipper is not responsible for delivery to the final destination (generaly the buyer’s facilities), or for buying insurance.
CIP – Carriage and Insurance Paid to (named place of destination). This term is broadly similar to the above CPT term, with the exception that the seller is required to obtain insurance for the goods while in transit.
DAT – Delivered at Terminal (named terminal at port or place of destination). This term means that the seller covers all the costs of transport (export fees, carriage, unloading from main carrier at destination port and destination port charges) and assumes all risk until destination port or terminal.
DAP – Delivered at Place (named place of destination)
Can be used for any transport mode, or where there is more than one transport mode. The seller is responsible for arranging carriage and for delivering the goods, ready for unloading from the arriving conveyance, at the named place. Duties are not paid by the seller under this term (an important difference from Delivered At Terminal DAT, where the buyer is responsible for unloading).
DDP – Delivered Duty Paid (named place of destination).
Seller is responsible for delivering the goods to the named place in the country of the buyer, and pays all costs in bringing the goods to the destination including import duties and taxes. The seller is not responsible for unloading.
FAS – Free Alongside Ship (named port of shipment).
The seller delivers when the goods are placed alongside the buyer's vessel at the named port of shipment. This means that the buyer has to bear all costs and risks of loss of or damage to the goods from that moment. The FAS term requires the seller to clear the goods for export, which is a reversal from previous Incoterms versions that required the buyer to arrange for export clearance.
FOB – Free on Board (named port of shipment).
The seller must advance government tax in the country of origin as of commitment to load the goods on board a vessel designated by the buyer. Cost and risk are divided when the goods are sea transport in containers.
CFR – Cost and Freight (named port of destination).
Seller must pay the costs and freight to bring the goods to the port of destination. However, risk is transferred to the buyer once the goods are loaded on the vessel. Insurance for the goods is NOT included. and This term is formerly known as CNF (C&F, C+F or CF).
CIF – Cost, Insurance and Freight (named port of destination)Exactly the same as CFR except that the seller must in addition procure and pay for the insurance.
PRACTICE:
2. Look up in a dictionary the Ukrainian equivalents for the following international trade terms and put them into the table:
| freight - | buyer - |
| cost - | seller - |
| insurance - | port of destination- |
| customs duty - | port of loading - |
| delivery - | free carrier - |
| shipment - | ex works - |
3. Study attentively the chart given below. Analyse where the a seller’s cost and risk finish and a buyer’s cost and risk start according to certain regulations. It will help you to answer the questions of the quiz and fill in the answer table:
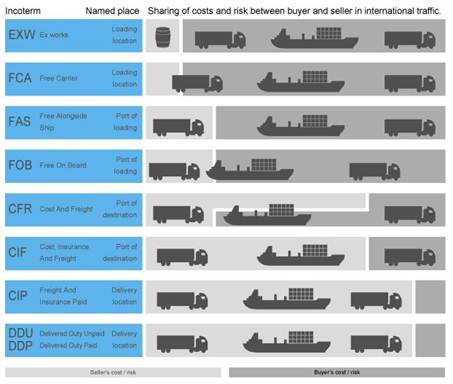 Incoterms quiz:
Incoterms quiz:
| 1. | 2. | 3. | 4. | 5. | 6. | 7. |
1. Which of the statements (2) about EXW are true?
a. The seller pays the transport costs up to the port of shipment.
b. The buyer pays transport costs from the seller's premises on.
c. The seller makes the goods available at his premises.
d. The buyer makes the goods available at his premises.
2. Which terms are cheapest for the seller?
| a. DDP b. CIF | c. FAS d. EXW |
3.What does FOB stand for?
a. billing
b. free on board
c. free original barbecue
4. Match the definition with the Incoterms: ‘The seller pays the transport costs up to the port of shipment. He bears the risk until the goods have passed the ship's rail at the port of shipment.’
| a. FOB b. FAS c. EXW | d. DDP e. CIF |
5. Which terms apply to DDP?
a. The seller pays all the costs and bears the risk until the goods have been delivered on his side of the border.
b. The seller pays insurance and transport costs up to the port of destination.
c. The seller pays all costs, including customs duty.
d. The buyer has to cover all the costs, including sea insurance and customs duty.
6. What does CIF include?
a. transport costs and customs duty
b. insurance and customs duty
c. transport cost and insurance
7. Free alongside ship (FAS) means that...
a. the goods don’t belong to anybody as long as they are alongside the ship.
b. the goods have to be delivered by sailboat.
c. the seller has to pay for the transport until the goods are being unloaded at the port of destination.
d. the buyer is responsible for the transportation of his goods as soon as they are being loaded aboard.
Тема 7
Поиск по сайту: