 |
АвтоАвтоматизацияАрхитектураАстрономияАудитБиологияБухгалтерияВоенное делоГенетикаГеографияГеологияГосударствоДомДругоеЖурналистика и СМИИзобретательствоИностранные языкиИнформатикаИскусствоИсторияКомпьютерыКулинарияКультураЛексикологияЛитератураЛогикаМаркетингМатематикаМашиностроениеМедицинаМенеджментМеталлы и СваркаМеханикаМузыкаНаселениеОбразованиеОхрана безопасности жизниОхрана ТрудаПедагогикаПолитикаПравоПриборостроениеПрограммированиеПроизводствоПромышленностьПсихологияРадиоРегилияСвязьСоциологияСпортСтандартизацияСтроительствоТехнологииТорговляТуризмФизикаФизиологияФилософияФинансыХимияХозяйствоЦеннообразованиеЧерчениеЭкологияЭконометрикаЭкономикаЭлектроникаЮриспунденкция
CHAPTER 3. COMBUSTION CHAMBER
|
Читайте также: |
3.1. PURPOSE AND DESIGN
The combustion chamber (fig.3.1, 3.2) is used for combustion of fuel in the airflow and for producing the operating gases. It is of annular shape with a fuel manifold equipped with 12 nozzles. The combustion chamber consists of a casing, an inner case of the diffuser, a flame tube and a fuel manifold.
The combustion chamber casing is a load-carrying engine element. In the front part together with the inner case it forms a diffuser (its purpose is to slow down speed of airflow).
On the casing of the combustion chamber the following units are located: II support oil scavenge line, drain valves, ignition plugs (2 in number), flame tube suspensions (9 in number), fuel manifolds suspensions (3 in number), air bleed pipe union for the de-icing system, air bleed pipes for HP-3 fuel regulating pump (2 in number), air bleed pipes for the ejector and engine pressure ratio indicator.
The inner case of the diffuser is essentially a profiled tube manufactured of a titanium alloy. It has 3 bandage rims (shrouds) used for rigidity.
The flame tube 8 of annular type consists of the following components: outer and inner fairings, 2 external and 2 internal sections, 12 swirlers, corrugating rings (between the section), 12 floating rings for nozzles installation.
The flame tube is of annular shape of welded construction. Its front part is fixed by means of 9 suspensions, and the tail part is floating (telescopic connection). Its purpose is to compensate components temperature expansion.
3.2. COMBUSTION CHAMBER OPERATION
In the flame tube fuel is atomized and mixed with air, as a result creating fuel-air mixture by mixing primary airflow (25%) supplied by swirlers with the fuel atomized by the nozzles (the proportion is 1 fuel weight part for 15…17 air weight parts). Duplex nozzles are used in this engine. Through the first fuel manifold fuel is supplied at all power settings and during engine start up. Through the second manifold air is supplied by the air СВ – 78 starter via pressurization valve for better fuel atomization and ignition.
In the process of engine start up fuel is ignited by two spark plugs. After start up sequence is over, the burning process continues due to the contact of newly supplied fuel-air mixture and hot gases.
If fuel pressure increases over 6 кg/сm2 in the first fuel manifold, pressurization valve of the second manifold is closed and fuel is then supplied to both manifolds.
The gas temperature in the area where burning process takes place reaches approximately
2500 ºС. By mixing this gas with the secondary airflow gas temperature before compressor turbine is reduced to the allowed value.
The diagram of burning process and dynamics of parameters change along combustion chamber air is indicated at fig. 3.1.
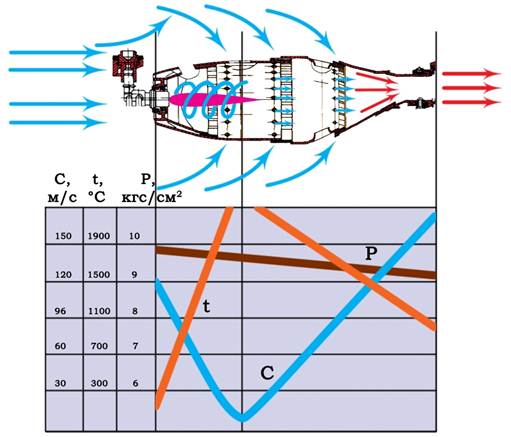

Рис. 3.1. Камера сгорания
1 – завихритель; 2 – внутренний корпус; 3 – топливный коллектор; 4 – форсунка;
5 – фланец подвода масла; 6 – подвеска; 7 – свеча зажигания; 8 – жаровая труба;
9 – наружный корпус диффузора; 10 –гофрированная прокладка; 11 – корпус турбины; 12 – вал турбины компрессора.


Fig. 3.1. Combustion chamber:
1 – swirler; 2 –inner casing; 3 – fuel manifold; 4 –; fuel nozzle; 5 – oil delivery flange; 6 – suspension; 7 –spark plug; 8 – flame tube; 9 – diffuser outer casing; 10 –corrugated spacer; 11 – turbine casing;
12 – compressor turbine shaft.
3.3. ВОЗМОЖНЫЕ НЕИСПРАВНОСТИ
1.Трещины ® прогар КС ® пожар на двигателе.
Причины:
- запуск неподогретого двигателя при t°нв≤ – 30°С;
- тепловой удар при форсировании холодного двигателя;
- невыдерживание временных ограничений на максимальных режимах;
- нарушение охлаждения двигателя (нагар, неполное сгорание топлива);
- отказ отдельных форсунок (плохой распыл из-за обгорания, перекоса, засорения);
- перегрев двигателя в полете;
- тепловой удар при выключении неохлажденного двигателя;
- отказ блока дренажных клапанов;
- отказ ускорительного клапана дозирующей иглы;
- применение некондиционного топлива.
При обнаружении прогара двигатель снимается с вертолета.
2.Срыв пламени ® отказ двигателя.
Причины:
- попадание на вход двигателя посторонних предметов;
- помпаж компрессора;
- падение давления топлива перед форсунками ниже минимально допустимого;
- резкое падение nтк, особенно на больших высотах.
3.4. ОСОБЕННОСТИ ЭКСПЛУАТАЦИИ
1. Определять по цветам побежалости при ТО вероятность прогара КС.
2. Контролировать качество заправки.
3. Подогревать двигатели при необходимости перед запуском до
t°м = – 15°С в редукторе, но не менее 20 минут.
4. Контролировать состояние вертолетных площадок на предмет отсутствия посторонних легких предметов.
5. Выполнять предполетный осмотр КС.
6. Соблюдать РЛЭ по запуску, прогреву (не менее 1 минуты) и выключению двигателей (охлаждение 1 – 2 или 2 – 3 минуты).
7. Контролировать и выдерживать в полете max t°г и время непрерывной работы на режимах ограничения.
8. Согласовывать темпы перемещения РОШ с приемистостью двигателя на переходных режимах.
9. Устанавливать заглушки в воздухозаборники сразу же после останова двигателей.
3.3. PROBABLE TROUBLES
1. Cracks ® combustion chamber burning out ® fire of the engine.
Reasons:
- start-up of the engine without warming at ambient air temperature lower then -30°C;
- thermal shock in case of power augmentation of the cold engine;
- if limitation time of operation at maximum ratings is not observed;
- improper cooling conditions (carbon deposit, incomplete combustion of fuel);
- failure of some fuel nozzles (imperfect fuel spray due to burning, misalignment or clogging);
- overheating of the engine in flight;
- thermal shock if the engine was not cooled before shut down;
- failure of drain valves block;
- failure of acceleration valve of the metering needle;
- use of sub-standard fuel;
In this case the engine should be replaced before its service life is over.
2. Flameout ® engine failure.
Reasons:
- foreign object ingestion;
- compression stall;
- fuel pressure drop below minimum permissible before the nozzles;
- sharp drop of turbo compressor RPM (nTC), especially at high altitude.
3.4. OPERATION PECULIARITIES
1. To inspect the combustion chamber for hot spots during technical maintenance. In this way it is possible to prevent burn out.
2. To check fuel quality.
3. To perform engines pre-heating before their start up until the oil in the gear box is heated up to -15ºC or not less than 20 minutes of pre-heating procedure.
4. To inspect the helicopter stand. It should be free of foreign light objects.
5. To perform preflight inspection.
6. To follow the directions of the Flight Manual as for engine start up, warming up (not less than 1minute) and engines shut down (to cool them for 1 -2 min or 2 – 3 min).
7. In flight to check and do not exceed max gas temperature and time of continuous operation at take off and nominal (METO) power rating.
8. To coordinate the rate of collective pitch control lever movement with acceleration time of the engine at transition ratings.
9. To install cover plugs immediately after engine shutdown.
Поиск по сайту: