 |
АвтоАвтоматизацияАрхитектураАстрономияАудитБиологияБухгалтерияВоенное делоГенетикаГеографияГеологияГосударствоДомДругоеЖурналистика и СМИИзобретательствоИностранные языкиИнформатикаИскусствоИсторияКомпьютерыКулинарияКультураЛексикологияЛитератураЛогикаМаркетингМатематикаМашиностроениеМедицинаМенеджментМеталлы и СваркаМеханикаМузыкаНаселениеОбразованиеОхрана безопасности жизниОхрана ТрудаПедагогикаПолитикаПравоПриборостроениеПрограммированиеПроизводствоПромышленностьПсихологияРадиоРегилияСвязьСоциологияСпортСтандартизацияСтроительствоТехнологииТорговляТуризмФизикаФизиологияФилософияФинансыХимияХозяйствоЦеннообразованиеЧерчениеЭкологияЭконометрикаЭкономикаЭлектроникаЮриспунденкция
Overhead transmission lines
58. Overhead AC transmission lines usually carry 3-phase current. The voltages can be different according to the particular grid system they belong to. Transmission voltages vary from 69 kv up to 765 kv.
59. The DC voltage transmission tower has lines in pairs rather than in threes (for 3-phase current) as in AC voltage lines. One line is the positive current line and the other is the negative current line. The picture shows the examples of different overhead transmission line structures in use today.
60. 
Some typical transmission line structures
61.
62. High-voltage overhead lines are made of aluminium wires not covered by insulation. Wires have several strands and are often reinforced with steel strands. Copper was sometimes used before for overhead transmission but aluminium weighs less and is cheaper. Overhead conductors can have cross sectional area from 12 mm2 to 750 mm2. Transmission voltages are usually 110 kV and above. Voltages 66 kV and 33 kV are sometimes used on long lines with small loads. Voltages less than 33 kV are usually used for distribution.
63. Insulators are usually made of porcelain or glass and can be stacked in a suspension insulator string. They hang from a cross arm on a tower or pole and support the line conductor. Suspension insulators are used for very high voltage systems.
64.
65.
66. 
67. Suspension insulators
68. 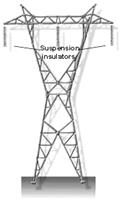
Suspension insulators on a tower
69.
70. 
71.
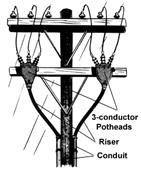
72. Riser pole
73. A pothead is a type of insulator with a bell or pot-like shape used to connect underground electrical cables to overhead lines. It separates the conductors from one another in the cable. It also seals the cable end from the weather. Potheads are mounted on a distribution pole.
74. 
Air circuit breaker
75. Air circuit breakers are used to break circuits while current flows through them. Compressed air is used to quench the arc when the connection is broken.
76. 
Bus support insulators
77.
78. Bus support insulators are porcelain or fiberglass insulators that serve to isolate the bus bar switches and other support structures and to prevent leakage current from flowing through the structure or to ground. These insulators are similar in function to other insulators used in substations and transmission poles and towers.
79. 
Oil circuit breakers in a 41 kV circuit
80. Oil circuit breakers are used to switch circuits and equipment in and out of a system in a substation. They are oil filled to provide cooling and to prevent arcing when the switch is activated.
81.
82. 
83. Capacitor bank
84. Capacitors are used to control the level of the voltage supplied to the customer by reducing or eliminating the voltage drop in the system caused by inductive reactive loads.
85.

Circuit switcher
86. Circuit switchers provide equipment protection for transformers, lines, cables, and capacitor banks. They also are used to energize and deenergize capacitor banks and other circuits.
87.
88. Task 1. Translate from Russian into English.
89. 1.Линии электропередачи используют трехфазный переменный ток.
90. 2. Линии электропередачи связаны в региональные, национальные или континентальные сети.
91. 3. Высоковольтные воздушные линии электропередачи используют алюминиевые провода, не покрытые изоляцией.
92. 4. Подземные линии электропередачи через кабели более дорогие, но часто используются в городах.
93. 5. Гирлянда подвесных изоляторов висит на поперечине вышки или на столбе и поддерживает линейный провод.
94. 6. Воздушные автоматические выключатели используются для прерывания цепи, когда в них течет ток. Когда контакт разрывается, они гасят дугу сжатым воздухом.
95.
96. Read the English words and their translation into Russian. Then cover the left column and translate the Russian words back into English.
97. emergency [I'mWGqnsI] авария, непредвиденный случай
98. leakage current ток утечки
99. to quench [kwenC]the arc гасить дугу
100. switcher переключатель
101. switching point переключательная подстанция
102. subtransmission line (distribution line) распределительная линия (отходящая от оконечной подстанции)
103. capacitor bank конденсаторная батарея
104. switchboard panel распределительный щит
105. power-line carrier высокочастотная связь по проводам ЛЭП
106. to energize ['enqGaIz] подавать питание; включать напряжение
107. control system система управления
108. bus шина (электрическая)
109. supervisory control диспетчерское управление; диспетчерский контроль
110. blackout полное отключение
111. residential customer бытовой потребитель (электроэнергии)
112. power transformer силовой трансформатор
113. underground cable подземный кабель
114. transformer vault [vLlt] трансформаторная будка
115. hollow ['hOlqu] пустой, полый
116. tube [tjHb] труба
117. shielded cable экранированный кабель
118. shielding экранирование
119. sheath [SJT] металлическая оплётка кабеля
120. jacket чехол, оболочка кабеля
121. inductive reactance индуктивное сопротивление
122. to house помещать
123. manhole смотровой колодец, люк
124. duct кабельный канал
125. conduit ['kOnduIt] кабелепровод
126.
127. Text 2
Substation
129. A substation is a high-voltage electric system facility. It is used to switch on and off generators, equipment, and circuits or lines in a system. It also is used to change AC voltages from one level to another, and/or change alternating current to direct current or direct current to alternating current. Some substations are small. They have a transformer and switches. Other substations are very large with several transformers and dozens of switches and other equipment.
130. 
131. Substation control house
132. The substation control house contains switchboard panels, batteries, battery chargers, supervisory control, power-line carrier, meters, and relays. The control house provides all weather protection and security for the control equipment. It is also called a doghouse.
133. 
134. Batteries
135. Batteries are used in the substation control house to power the control systems in case of a power blackout.
136.
137. 
Substation control panel
138. Control panels contain meters, control switches and recorders located in the control building, also called a doghouse. These are used to control the substation equipment, to send power from one circuit to another or to open or to shut down circuits when needed.
139. 
Substation control panel relays
140. Relays in substation control panelare used to trigger circuit breakers and other switches in substations and transmission and distribution systems.
141.
142.
143. Substation Types:
144. 1. A step-up transmission substation receives electric power from a nearby power plant and uses a large power transformer to increase the voltage for transmission to distant places. A transmission bus is used to distribute electric power to one or more transmission lines.
145. A substation can have circuit breakers that are used to switch generation and transmission circuits in and out of service. This is made in case of emergencies requiring shut-down of power to a circuit or redirection of power.
146. The voltages from a step-up transmission substation are determined by the customer needs in regional grids. Typical voltages are:
High voltage (HV) ac: 69 kV, 115 kV, 138 kV, 161 kV, 230 kV
147. Extra-high voltage (EHV) ac: 345 kV, 500 kV, 765 kV
148. Ultra-high voltage (UHV) ac: 1100 kV, 1500 kV
149. Direct-current high voltage (dc HV): ±250 kV, ±400 kV, ±500 kV
150. Direct current voltage is either positive or negative polarity. A DC line has two conductors, so one would be positive and the other negative.
151.
152. 
Step-up AC transmission substation
153.
154. 2. Step-down transmission substations are located at switching points in an electrical grid. They connect different parts of a grid and are a source for subtransmission lines (distribution lines). The step-down substation can change the transmission voltage to a subtransmission voltage, usually 69 kV. The subtransmission voltage lines can then serve as a source to distribution substations. The power goes to a distribution substation.
155.
156. 
Step-down transmission substation
157.

Step-down power transformer
158.
159. 3. Distribution substations are located near to the end-users. Distribution substation transformers change the transmission voltage to lower levels for use by end-users. Typical distribution voltages vary from 34,500Y/19,920 volts to 4,160Y/2400 volts.
160. 34,500Y/19,920 volts means a three-phase circuit with a grounded neutral source. This would have three high-voltage conductors or wires and one grounded neutral conductor, a total of four wires. The voltage between the three phase conductors or wires would be 34,500 volts and the voltage between one phase conductor and the neutral ground would be 19,920 volts.
161. From distribution substation the power is distributed to industrial, commercial, and residential customers.
162.
163. 
Distribution substation
164.
165. Underground distribution substations are also located near to the end-users. Distribution substation transformers change the subtransmission voltage to lower levels for use by end-users. Typical distribution voltages vary from 34,500Y/19,920 volts to 4,160Y/2400 volts.
166. An underground system may consist of these parts:
167.
168. 
169.
Поиск по сайту: